Computer Basics. What is a Computer and Generations of Computer – Part 1
What is computer??
- Is a machine and is a multipurpose tool
- Which does computations–“Calculations and Comparisons”
- Converts data into Information.
- Information is useful form of data.
Why??
- Increase computational capacity, huge calculations etc.,
- Analysis of complex problems.
Full form of COMPUTER?
Commonly Oriented Machine Particularly Used For Trade Education and Research.
Characteristics of Computer
- Speed – about 3 million calculations per second
- Accuracy – never wrong
- Reliability – as long as input is reliable output is always reliable.
- Memory/Storage Capacity – large volumes of data.
- Versatility – different tasks , can accept/give out info via various input out divides
- Automation – once input given rest it do thing on its own
- Diligence – no distress or laziness or repetitive operations.
- Convenience – easy to access
- Flexibility – can be used for multipurposed like games, movies, songs, coadding etc.
But has no intuition – cannot take self decisions (cognitive thinking) which humans have. But a computer can only proceed as it has been programmed and designed to.
E.g., -if not graphics card is installed in computer you will not be able to use Desktop.
E.g., –if not audio card are embedded In computer Your speaks wont work
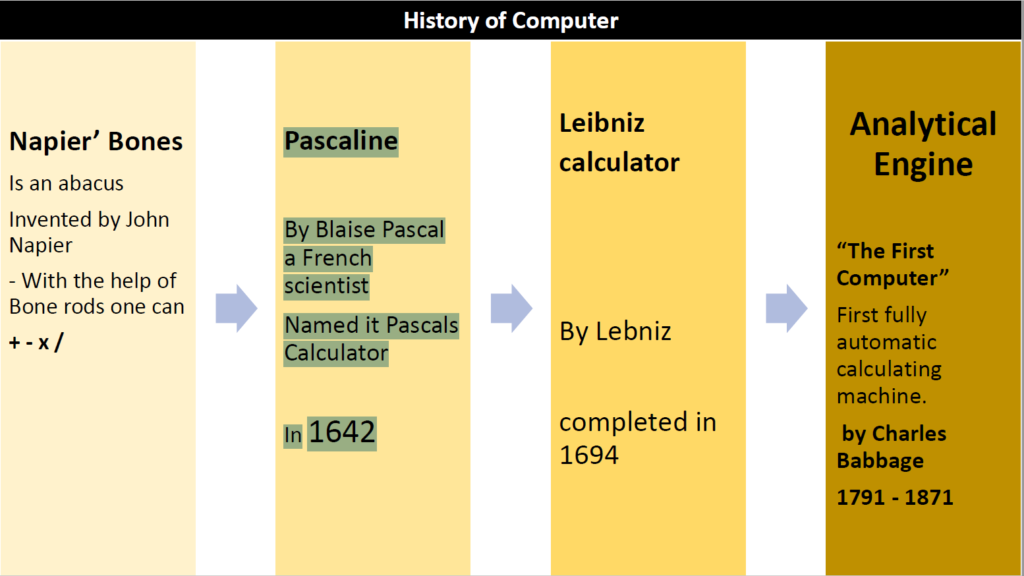
Five generations of Computer
First Generation of Computers
- Used for period from(1942-1955)
- The beginning of commercial computer age is from UNIVAC(UniversalAutomaticComputer).
- They were based on vacuum tubes .(only electronic component available at that time)
- Examples of first generation computers are
- ENIVAC(Electronic numerical indicator and calculator)
- UNIVAC-1.
Disadvantages:
- Large in size.
- consumed More energy.(and heat up)
- Non-portable(costlier and not of much use)
- Limited commercial use
- Very slow speed
- Used machine language only(0and1)
- Used magnetic drums which provide very less data storage.
Advantages:-
- Vacuum tube technology made possible to make electronic digital computers that exists today.
Second Generation Computers(1955-1964)
- used transistors. (The size of the computers was decreased by replacing vacuum tubes with transistors.)
- The examples of second generation computers are
- IBM7094series,IBM1400seriesand CDC164 etc.
Advantages :
- Smaller in size as compared to the first generation computers.
- Used less energy and were not heated.
- Better speed and could calculate data in microseconds
- Used faster peripherals like tape drives, magnetic disks, printer etc.
- Used Assembly language instead of Machine language.
Disadvantages :
- Cooling system was required
- Constant maintenance was required
- Only used for specific purposes (not versatile )
- Still Costly
Third Generation Computers(1964-1975)
Used the integrated circuits (IC).
- The first IC was invented and used in 1961.
- A single IC chip may contain thousands of transistors.
- The computer became smaller in size, faster, more reliable and less expensive.
- The examples of third generation computers are
IBM370,IBM System/360, UNIVAC1108 and UNIVAC AC 9000 etc.
An integrated circuit (IC), sometimes called a chip or microchip, is a semiconductor wafer on which thousands or millions of tiny resistors, capacitors, and transistors are fabricated.
Advantages :
- Smaller in size as compared to previous generations.
- More reliable. Used less energy.
- Better speed and could calculate data in nanoseconds.
Disadvantages :
- Air conditioning was required.
- IC chips –needs highly sophisticated technology.
Fourth Generation Computers (1975-Present)
Used Microprocessor.
- The Microprocessor contains thousands of ICs.
- The LSI (Large Scale Integration) circuit and VLSI (Very Large Scale Integration) circuit was designed.
- It greatly reduced the size of computer.
- The size of modern Microprocessors is usually one square inch.
- It can contain millions of electronic circuits.
- PC.
Advantages :
- More powerful and reliable than previous generations.
- Small in size
- Fast processing power with less power consumption
- Fan for heat discharging and thus to keep cold.
- Cheapest among all generations
- All types of High level languages can be used in this type of computers
Disadvantages :
- The latest technology is required for manufacturing of Microprocessors.
Fifth Generation Computers(Present& Beyond)
- Scientists are working hard on the 5th generation computers with quite a few breakthroughs and achievements.
- based on Artificial Intelligence (AI).
- Computers can understand spoken words & imitate human reasoning.
- IBM Watson computer is one example that outsmarts Harvard University Students.

Other key points:
- Notebook computer are also called Ultra Book.(extremely lightweight and portable)
- Palmtop are computers that fits on your Palm.
- Smart Phones are cellular phones that function both as a phone and as a small PCs.
- Computers connect together to form a Network.
- Personal computers are designed to meet the computing needs of an Individual.
- A super computer contains thousands of Microprocessors.
| Father of computer | Charles Babbage |
| Father of Computer Science | Alan Turing |
| First commercial available computer | Universal Automatic Computer |
| Fastest super computer in india | Pratyush |
| First Super Computer in India | Param 8000 |
| First super computer in the world | Cray CDC 600 |
| Fastest Super computer in the world | Summited by theUSA |
